Knee | Total Knee Arthroplasty: How to perform
Last updated on August 1 2024
Description
The total knee arthroplasty (TKA) allows estimating the distal femoral cut and proximal tibial cut perpendicular to the mechanical axis and the tibiofemoral angle. This is able to be used when the full leg appears in medical imaging. Thus, it is possible to observe the mechanical axis of the leg and to know the total length, as well as the femur and tibia lengths.
Measurements
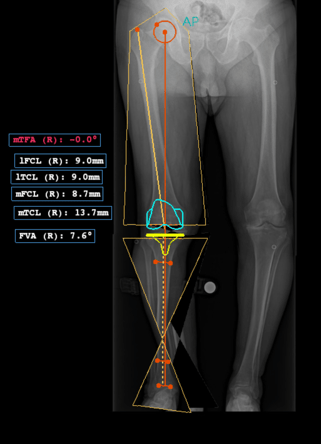
The measurements made by the procedure are displayed in the image::
- Mechanical Tibiofemoral Angle (mTFA): the angle between the line from the center of the femoral head to the center of the femoral articular surface and the line from the center of the tibial plateau to the center of the tibial distal articular surface;
- Lateral Femoral Cut Length (lFCL): a lateral length in the femur to perform the resection;
- Lateral Tibial Cut Length (lTCL): a lateral length in the tibia to perform the resection;
- Medial Femoral Cut Length (mFCL): a medial length in the femur to perform the resection;
- Medial Tibial Cut Length (mTCL): a medial length in the tibia to perform the resection;
- Femoral Valgus Angle (FVA): the angle between the mechanical and anatomical axis of the femur.
Auxiliary references
To show this procedure, PeekMed® needs additional references:
- Mechanical Axis of the Femur (MAF): femur length, i. e., the length between the center of the femoral head and the midpoint of the femur plateau;
- Anatomical Axis of the Femur (AAF): line from the center of the proximal femur to the center of the distal femur;
- Mechanical Axis of the Tibia (MAT): tibial length, i. e., the length between the tangent line of the tibial distal articular surface and the midpoint of the tibial plateau;
- Anatomical Axis of the Tibia (AAT): line from the center of the proximal tibia to the center of the distal tibia;
- Mechanical Axis (MA): total leg length, i. e., the length between the center of the femoral head and the tangent line of the tibial distal articular surface.
How to perform
With automatic landmark detection
After selecting the procedure in the sidebar, as well as the side where you will perform the procedure, PeekMed will analyse the image and detect the landmarks.
If the detection is successful, the landmarks will be placed automatically. You can adjust them before approving the placement.
If it's not possible to detect the landmarks automatically, you will be prompted to place them manually.
You can enable/disable the automatic landmark detection in Settings.
Without automatic landmark detection
After selecting this procedure in the sidebar, as well as, the side where you will perform the procedure, you must mark the points to conclude it. To see the caption of each point you need to click on this button .
Beware: you can change the position of the points at this stage or later. To do this, simply click on each handle with the left mouse button and move them to the most suitable position.
This procedure cannot be performed simultaneously with AP Knee Resection as the latter contains all of its points.
For advanced configuration, please follow the instructions below.
Advanced Configuration
With the advanced configuration of this procedure it is possible to automatically insert a femoral and tibial template and perform the auto resection of the knee.
To initiate the advanced configuration you need to click the button in the object card. PeekMed will then check the local database to validate if all required templates are present. If there is one or more templates missing from a specific system you are prompted to download the ones that are missing, as you can see in the image below.

Clicking “Yes” will direct you to the download manager and show you the templates that are available for this procedure.
You can then select the ones you want to work with and download them.
When you have at least one complete template system you can then start the configuration. The first step will be to choose the template manufacturer for the system you are going to use.
If you haven't downloaded all the available templates you can click the "Download more" button to access the download manager again.

After clicking start you will be able to select the femoral and tibial components as well as their parameters.

|

|
When you click "Finish", PeekMed will then validate the components selections, place them
in the planning and restore the patient’s femoral and tibial anatomical alignment, by
performing a femoral and a tibial cut and moving until their axes are aligned.
All these steps are demonstrated in the video below.